What is a Break-Even Point and How to Calculate
If the same cost data are available as in the example on the algebraic method, then the contribution is the same (i.e., $16). Using the algebraic method, we can also identify the break-even point in unit or dollar terms, as illustrated below. Or, if using Excel, the break-even point can be calculated using the “Goal Seek” function. If a company has reached its break-even point, the company is operating at neither a net loss nor a net gain (i.e. “broken even”).
When companies calculate the BEP, they identify the amount of sales required to cover all fixed costs before profit generation can begin. The break-even point formula can determine the BEP in product units or sales dollars. Break-even analysis compares income from sales to the fixed costs of doing business. The five components of break-even analysis are fixed costs, variable costs, revenue, contribution margin, and break-even point (BEP). A firm with lower fixed costs will have a lower break-even point of sale and $0 of fixed costs will automatically have broken even with the sale of the first product, assuming variable costs do not exceed sales revenue. Generally, to calculate the breakeven point in business, fixed costs are divided by the gross profit margin.
All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. It is only useful for determining whether a company is making a profit or not at a given point in time. The break-even point or cost-volume-profit relationship can also be examined using graphs.
Where Should We Send Your Answer?
A break-even point analysis is used to determine the number of units or dollars of revenue needed to cover total costs (fixed and variable costs). The break-even point is the volume of activity at which a company’s total revenue equals the sum of all variable and fixed costs. The break-even point is the point at which there is no profit or loss. Calculating the breakeven point is a key financial analysis tool used by business owners. Once you know the fixed and variable costs for the product your business produces or a good approximation of them, you can use that information to calculate your company’s breakeven point. Small business owners can use the calculation to determine how many product units they need to sell at a given price point to break even.
Businesses share the similar core objective of eventually becoming profitable in order to continue operating. Otherwise, the business will need to wind-down since the current business model is not sustainable. All of your raw financial information flows into it, and useful financial information flows out of it. For more cost cutting ideas, check out our guide of 25 ways to cut costs. If you’re having trouble hitting your break-even point or it seems unreachable, it’s time to make a change.
Call Option Breakeven Point Example
Break-even analysis, or the comparison of sales to fixed costs, is a tool used by businesses and stock and option traders. It is essential in determining the minimum sales volume required to cover total costs and break even. If the company can increase its contribution margin per unit to $8 (by perhaps lowering its per unit variable cost), it only needs to sell 8,750 ($70,000 / $8) to break even. It is also possible to calculate how many units need to be sold to cover the fixed costs, which will result in the company breaking even. To do this, calculate the contribution margin, which is the sale price of the product less variable costs. Therefore, given the fixed costs, variable costs, and selling price of the water bottles, Company A would need to sell 10,000 units of water bottles to break even.
At the break-even point, the total cost and selling price are equal, and the firm neither gains nor losses. The Break-Even Point (BEP) is the inflection point at which the revenue output of a company is equal to its total costs and starts to generate a profit. Break-even analysis looks at fixed costs relative target cost versions in variance calculation to the profit earned by each additional unit produced and sold.
Submit to get your question answered.
Another limitation is that the breakeven point assumes that sales prices, variable costs per unit, and total fixed costs remain constant, which is often not the case. The price of goods sold at fluctuates, and the cost of raw materials may hardly stay stable. In addition, changes to the relevant range may change, meaning fixed costs can even change.
Another very important aspect that needs to address is whether the products under consideration will be successful in the market. Consider the following example in which an investor pays a $10 premium for a stock call option, and the strike price is $100. The breakeven point would equal the $10 premium plus the $100 strike price, or $110. On the other hand, if this were applied to a put option, the breakeven point would be calculated as the $100 strike price minus the $10 premium paid, amounting to $90.
Here’s the basics you need to know to stay on top of your books and taxes. Here’s how to calculate gross, operating, and net profit margins and what they can tell you about your business. “When will we actually make money?” is the burning question for new businesses. Fortunately, you can answer this question by calculating your break-even point. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.
The breakeven point is the production level at which total revenues for a product equal total expenses. The breakeven point can also be used in other ways across finance such as in trading. In other words, it is used to assess at what point a project will become profitable by equating the total revenue with the total expense. At this point, you need to decide whether the current plan is feasible or whether the selling price needs to be raised or whether the operating cost needs to be controlled or both the price and the cost needs to be revised.
A Guide to Nonprofit Accounting (for Non-Accountants)
The formula for break-even point (BEP) is very simple and calculation for the same is done by dividing the total fixed costs of production by the contribution margin per unit of product manufactured. Assume a company has $1 million in fixed costs and a gross margin of 37%. In this breakeven point example, the company must generate $2.7 million in revenue to cover its fixed and variable costs. To find your variable costs per unit, start by finding your total cost of goods sold in a month. If you have any other costs tied to the products you sell—like payments to a contractor to complete a job—add them to your cost of goods sold to find your total variable costs. Break-even analysis assumes that the fixed and variable costs remain constant over time.
- In other words, the breakeven point is equal to the total fixed costs divided by the difference between the unit price and variable costs.
- Calculating the breakeven point is a key financial analysis tool used by business owners.
- There is no net loss or gain at the break-even point (BEP), but the company is now operating at a profit from that point onward.
- The break-even point (BEP) is the amount of product or service sales a business needs to make to begin earning more than you spend.
- In contrast to fixed costs, variable costs increase (or decrease) based on the number of units sold.
A business would not use break-even analysis to measure its repayment of debt or how long that repayment will take. If the price stays right at $110, they are at the BEP because they are not making or losing anything. Options can help investors who are holding a losing stock position using the option repair strategy. If sales drop, then you may risk not selling enough to meet your breakeven point. In the example of XYZ Corporation, you might not sell the 50,000 units necessary to break even.
It is also helpful to note that the sales price per unit minus variable cost per unit is the contribution margin per unit. For example, if a book’s selling price is $100 and its variable costs are $5 to make the book, $95 is the contribution margin per unit and contributes to offsetting the fixed costs. This margin indicates how much of each unit’s sales revenue contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit once fixed costs are met. For example, if a product sells for $10 but only incurs $3 of variable costs per unit, the product has a contribution margin of $7. Note that a product’s contribution margin may change (i.e. it may become more or less what is credit mix efficient to manufacture additional goods).
- Published in Bookkeeping
How to Create a Master Budget
This means that components of master budget must be prepared in a specific order. We have ordered the above list in such a way that the necessary information needed by any component budget is provided by a preceding component. Suppose that you are part of a team that is responsible for creating ABC Corporation’s Master Budget.

What Should be Included in a Master Budget?
Preparing a master budget involves several steps, such as creating the sales forecast, production plan, and marketing budget. The finance team must ensure that all these steps are completed accurately and on time. The operating budget includes the expenses and revenue generated from the day-to-day business operations of the company. The operating budget focuses on the operating expenses, including cost of goods sold (COGS) and the revenue or income.
Join 41,000+ Fellow Sales Professionals

Master budget accounting becomes a tool for the management to identify its goals well in advance and channel the organization’s resources towards them. It should be noted that the budget should be prepared with the utmost caution as it affects the operational performance of the entire organization. This can occur when businesses fail to consider all the costs of running their operations, such as marketing, maintenance, what is a master budget and employee salaries. To avoid this mistake, businesses should thoroughly review their expenses and ensure they have included all relevant costs in their budget. The master budget should be reviewed regularly to align with the company’s strategic goals. This includes monitoring progress toward achieving the goals and making adjustments as necessary to ensure that the budget supports the strategic objectives.
Static Budget
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. This is because of the fact that they require certain planning, and changing one variable lead to changes in almost all parameters. Therefore, they cannot be changed once prepared, and it is really hard to account for these changes.

Cost Accounting
Firstly, it can be seen that Master Budgets cannot be changed over the course of time. This is really helpful in cases where there are strategic changes required in order to change the predicted outcome of the company. It can be seen that Master Budgets are required to establish a clear-cut idea regarding the financial status of the company. In this regard, it is also imperative that companies plan their liquidity position accordingly so that there are no operational backlogs during the course of the year.

It usually coincides with the fiscal year of the firm and can be broken down into quarters and further into months. If the firm plans for the master budget to roll from year to year, then it would usually add an extra month to the end of the budget to facilitate planning. A flexible budget can help companies account for both variable and fixed expenses, creating a more dynamic process and leading to more accurate forecasts. The flexible budget is compared to the company’s static budget to identify any variances (or differences) between the forecasted spending and the actual spending. Cash flow budgets help to examine past practices to examine what’s working and what’s not and make adjustments.
Master Budget vs. Flexible Budget
COGS is the cost of direct labor and direct materials that are tied to production. For instance, a machine shop should consider current cash flows, current loan rates, current debt limits, and future expected sales before management plans a large expansion. A master budget is a detailed financial plan that includes projections of sales, expenses, and profits for a specific period.
- The cash budget is a quarterly record of all money that comes in and goes out of the company, categorized by spending type.
- This involves evaluating the budget against the business’s strategic objectives, financial goals, and performance targets.
- It measures performance, and this helps the company to improve its performance over the course of time.
- Master Budgets tend to give companies a clear sense of direction and approach that can be used as an increasingly important planning tool.
- More specifically, it compiles the business units’, departments’, and cost centers’ expectations and consolidates them in Budgeted financial statements.
- Essentially, viewed from a different angle, the Master Budget consists of the firm’s projected Income Statement, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement for the upcoming years.
- This includes protecting sensitive financial information from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Flexible budgets are useful to have when sales exceed (or underperform) expectations.
- If the firm plans for the master budget to roll from year to year, then it would usually add an extra month to the end of the budget to facilitate planning.
- First, it provides a holistic view of the organization’s financial activities, enabling managers and executives to make informed decisions based on the available financial resources.
- Published in Bookkeeping
A credit is not a normal balance for what accounts?
For contra-asset accounts, the rule is simply the opposite of the rule for assets. Therefore, to increase Accumulated Depreciation, you credit it. While there are two debit entries and only one credit entry, the total dollar amount of debits and credits are equal, which means the transaction is in balance. Furthermore, let’s consider the below-mentioned http://isha.at/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=720 examples. A debit without its corresponding credit is called a dangling debit.
Which accounts normally have debit balances?
- The brokerage account with short positions possesses a normal credit balance, that can be refunded, while the one with long positions has a debit balance.
- If an account has a Normal Credit Balance, we’d expect that balance to appear in the Credit (right) side of a column.
- In order to correctly calculate credits and debits, a few rules must first be understood.
- This transaction will require a journal entry that includes an expense account and a cash account.
- Income has a normal credit balance since it increases capital.
Some specific examples of accounts with normal credit balances include accounts payable, loans payable, accrued expenses, retained earnings, and sales revenue. These accounts play a crucial role in proper financial reporting and decision-making. Understanding the concept of normal credit balances and the different types of accounts that fall into this category is essential for individuals and businesses navigating the world of finance.
Wrapping Up: The Normal Balance of an Accounts
- These accounts, like debits and credits, increase and decrease revenue, expense, asset, liability, and net asset accounts.
- A contra expense account is an account in the ledger that counterbalances another particular expense account and sustains the matching principle of accounting.
- For instance, asset sales, the dividend declared, consulting services, and interest income.
- Now that we have a basic understanding of credit balances, let’s explore the different types of accounts that typically have normal credit balances.
- The normal balance shows debit in the accounts payable when the left side is positive.
- For a credit account, the contra account is a debit account, and for a debit account, the contra account is a credit account.
These statements provide a snapshot of an organization’s financial health, and knowing which accounts have http://nerzhul.ru/technology/364.htmls is essential for accurate financial reporting. This transaction will require a journal entry that includes an expense account and a cash account. Note, for this example, an automatic off-set entry will be posted to cash and IU users are not able to post directly to any of the cash object codes. Because postage was purchased for $12.70, cash, an asset account, will be credited, which will decrease the cash balance by $12.70.
Record the Sale of a Fixed Asset
Sometimes, the profit from selling the product from the supplier is also debited by the company. In this case, the revenue generated from the sale of the product from the supplier is usually shown as a credit on the accounts payable. This is how it is done in the double-entry bookkeeping method. A normal balance is the side of the T-account where the balance is normally found. When an amount is accounted for on its normal balance side, it increases that account.
- A contra account is one which is offset against another account.
- Liability and capital accounts normally have credit balances.
- This general ledger example shows a journal entry being made for the payment (cash) of postage (expense) within the Academic Support responsibility center (RC).
- That is to say, the capital account tracks retained earnings throughout one accounting period to another.
After receiving advance payment, you’d need to mark it in accounts receivable as a credit balance. The expenses and losses are also debited on the normal balance of the accounts payable of a company’s balance sheet. This accounting equation is used to determine the normal balance of not only accounts payable but also accounts receivables. Expense accounts normally have debit balances, while income accounts have credit balances. Credit balance or net balance is the final amount (positive or negative) mentioned to the right of the ledger in accounting.
Normal Balance and the Accounting Equation
This usually happens when the company extends credit to its suppliers; the credit is reported as an expense. The expense shifts the balance of the https://seobiglist.com/category/marketing/page/2/ accounts payable from the credit side to the debit side. Knowing the normal balances of accounts is pivotal for recording transactions correctly.
If the figures are not the same, something has been missed or miscalculated and the books are not balanced. One of the fundamental principles in accounting is the concept of a ‘Normal Balance‘. Whether you’re an entrepreneur or a seasoned business owner, understanding the normal balance of accounts is crucial to keeping your business’s financial health in check. A current asset account that reports the amount of future rent expense that was paid in advance of the rental period. The amount reported on the balance sheet is the amount that has not yet been used or expired as of the balance sheet date. By having many revenue accounts and a huge number of expense accounts, a company will be able to report detailed information on revenues and expenses throughout the year.
What are the Normal Balances of each type of account?
It helps identify errors in the accounting system and ensures that financial transactions are recorded correctly. Knowing the normal balance of an account helps you understand how to increase and decrease accounts. Next, we’ll move on to adjusting these accounts with journal entries. An abnormal balance can indicate an accounting or payment error; cash on hand should never have a net credit balance, since one cannot credit (pay from) cash what has not been debited (paid in).
- Published in Bookkeeping
Accounts Payable Journal Entry Example
Accounts payable turnover refers to the ratio which measures the speed at which your business makes payments to its creditors and suppliers, indicating the short-term liquidity of your business. A sub-ledger consists of the details of all individual transactions of a specific account like accounts payable, accounts receivable, or fixed assets. The total of all these individual transactions can then be recorded in the general ledger. Accounts payable, if managed effectively, indicates the operational effectiveness of your business. Accounts payable management is essential when running a small business, because it ensures that your accounts payable contributes positively towards your business’s cash flows.
Accounts payable journal entry
When the bill is paid, the accountant debits accounts payable to decrease the liability balance. The offsetting credit is made to the cash account, which also decreases the cash balance. Accounts payable journal entries are made in an accounts payable ledger whenever a transaction relates to a purchase from a supplier made on credit. You can calculate the accounts payable by generating accounts payable aging summary report, if you are using QuickBooks Online Accounting Software.
Business Travel Expenses
- You need to keep a track of your accounts payable to know when the payments are due, so you can make the payments to your suppliers on time.
- When using the indirect method to prepare the cash flow statement, the net increase or decrease in AP from the prior period appears in the top section, the cash flow from operating activities.
- From the example above, ABC Ltd. purchased inventory for $1,500 on credit from XYZ Supply Co., one of its regular suppliers.
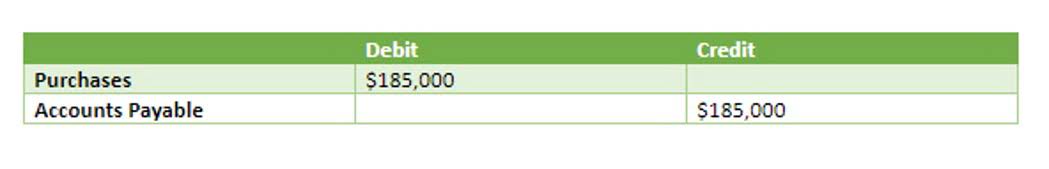
On the other hand, accounts payable refers to the amount you owe to your suppliers for goods or services received from them. Thus, the purchases account gets debited, and the accounts payable account gets credited. Furthermore, it is recorded as current liabilities on your company’s balance sheet.
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
However, small companies with low transaction volume don’t maintain special journals. These companies record their purchase transactions in general journal, along with other transactions. Companies mostly find it convenient to record an accounts payable liability when they actually receive the goods.
While payroll is not included in AP, it appears on the balance sheet as another of the business’s current liabilities. AP encompasses any amount of money a company owes besides payroll, including goods or services purchased, software subscriptions, logistics, late fees, or office utility bills. For instance, 20/10 net 30 is a trade credit that your suppliers offer for the sale of goods or services.
However, in certain situations, the title to goods passes to the buyer before the physical delivery is taken by him. In such situations, the liability should be recorded at the time of passage of title. Accounts payable are usually divided into two categories – trade accounts payable and other accounts payable. The goods that are not merchandise are the goods that the business does not normally deals in.
If your vendors create and send invoices using an invoicing software, then the invoice details will get uploaded to your accounting software automatically. However, if your vendors create and send invoices manually, then you’ll need to manually fill in the details in your accounting software or books of accounts. You as a business can be viewed top 11 small business accounting tips to save you time and money as a supplier, and your accounts receivables represent the amount of money you lend to your customers. Likewise, you are also a customer of your vendors and your accounts payable represent your borrowings from such suppliers. At the corporate level, AP refers to short-term payments due to suppliers. The payable is essentially a short-term IOU from one business to another business or entity.
The other party would record the transaction as an increase to its accounts receivable in the same amount. To help illustrate how accounts payable journal entries work, let’s look at five examples of when you’d make a journal entry and what it would look like. Accounts Payable (AP) is an accounting term that refers to money owed to suppliers, vendors, or employees for goods or services purchased on credit. It could refer to an account on a company’s general ledger, a department, or a role. Yet, no matter where the term appears, it’s always related to the amount of money a business owes to other entities within a specific timeframe. The accounts payable department also works to reduce costs by developing strategies to save a business money.
Reviewing Bill Details
In double-entry accounting, every transaction is made up of debits and credits. Small expenses such as miscellaneous postage, out-of-pocket office supplies or company meeting lunch are handled as petty cash. AP often handles a supply of sales tax exemption certificates issued to managers to ensure qualifying business purchases don’t include sales tax expenses.
What is your current financial priority?
The Company’s Accounting Department records payments made toward the invoice in their AP ledger and periodically reconciles this with statements received from suppliers. An increase in the accounts payable indicates an increase in the cash flow of your business. This is because when you purchase goods on credit from your suppliers, you do not pay in cash.
For example, paying an invoice within a discount period that many vendors provide. A company’s Accounts Payable department tracks the amounts owed and records them as short-term obligations on the general ledger. They are also responsible for keeping these records up-to-date and ensuring that invoices get paid by the payment date. Accounts Payable refers to a business’s obligations to suppliers and creditors for purchases made on an open account. It specifically refers to any amounts owed expected to be paid within branches of accounting one year or less (usually due in 30 to 60 days).
Taxes payable refer to the company’s federal, state, and local obligations. Every accounts payable department has a process to follow before making a vendor payment — this is the accounts payable process. Concrete guidelines are essential because of the value and volume of transactions during any period.
- Published in Bookkeeping


